European Foulbrood Treatment And Management for Beekeepers’ Success
European Foulbrood is a serious disease affecting honeybee larvae. It can weaken or kill entire colonies.
Beekeepers face many challenges, and European Foulbrood is one of the most daunting. This bacterial infection spreads quickly and can be devastating if not managed properly. Understanding how to treat and manage this disease is crucial for the health of your bees and the productivity of your hive.
In this guide, we will explore effective treatments and management strategies for European Foulbrood. By knowing the signs and taking prompt action, you can protect your bees and ensure a thriving hive. Stay with us to learn how to keep your bees healthy and your honey flowing.

Credit: www.mannlakeltd.com
Introduction To European Foulbrood
European Foulbrood (EFB) is a bacterial disease that affects honeybee larvae. This disease is caused by the bacterium Melissococcus plutonius. EFB can significantly impact beekeeping operations by weakening or even destroying bee colonies. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and transmission of EFB is crucial for effective management.
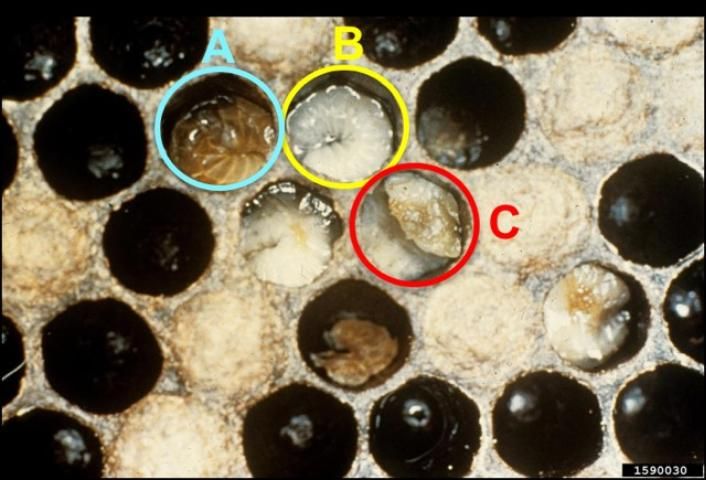
Symptoms Of Efb
The symptoms of European Foulbrood can vary. Here are the most common signs:
- Larvae appear twisted or curled.
- Discolored larvae, often yellow or brown.
- Larvae may have a sour odor.
- Pupae fail to reach the capped stage.
Identifying these symptoms early can help in managing and treating the disease effectively.
Causes And Transmission
European Foulbrood is caused by the bacterium Melissococcus plutonius. The disease spreads through infected larvae and contaminated equipment. Worker bees can also spread the bacteria while feeding larvae.
Transmission occurs primarily through:
- Feeding larvae with infected food.
- Using contaminated beekeeping equipment.
- Drifting bees from infected colonies.
Preventing the spread of EFB involves maintaining good hygiene and regular inspection of colonies.
Credit: edis.ifas.ufl.edu
Early Detection Techniques
Early detection of European Foulbrood (EFB) is crucial in managing this bee disease. Timely identification can save colonies and prevent widespread infection. Here, we explore two effective early detection techniques.
Visual Inspections
Regular visual inspections help in spotting early signs of EFB. During these inspections, look for larvae that appear twisted or have an unusual color. Healthy larvae are white and plump, while infected larvae may look yellow or brown. Inspect the brood cells carefully. Infected cells often have a sunken cap or may be partially open. Note any unusual odors. EFB can produce a sour smell. Consistent checking can help you catch the disease early.
Diagnostic Tools
Using diagnostic tools adds another layer of accuracy. Field test kits can provide quick results. These kits involve taking a sample from the affected brood and mixing it with a reagent. The color change indicates the presence of the disease. Laboratory tests offer more precise results. Send samples to a lab for detailed analysis. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests are highly accurate and can detect EFB even in early stages. Combining visual inspections with diagnostic tools ensures a comprehensive approach to early detection.
Preventive Measures
Preventing European Foulbrood (EFB) in bee colonies is crucial. It helps maintain healthy and productive hives. There are several effective preventive measures beekeepers can implement. These measures reduce the risk of EFB outbreaks and promote bee health.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene is essential. Clean beekeeping equipment regularly. Use disinfectant solutions to sanitize hive tools and boxes. Burn or discard heavily contaminated equipment. Avoid moving frames between colonies to prevent cross-contamination. Keep the apiary clean and remove dead bees promptly. This reduces the likelihood of spreading the disease.
Resistant Bee Strains
Choose bee strains that show resistance to European Foulbrood. Some bee breeds have natural resistance to diseases. Research and select these resistant strains for your apiary. Introduce queens from resistant stock into your colonies. This can enhance the overall resilience of your hives. Monitor the performance of these resistant strains regularly. Ensure they continue to thrive and resist EFB.

Credit: www.mannlakeltd.com
Treatment Options
European Foulbrood (EFB) can be a serious issue for beekeepers. Proper treatment and management are essential for maintaining healthy colonies. There are several treatment options available to handle this disease effectively.
Antibiotic Treatments
Antibiotics are a common method to treat EFB. The most frequently used antibiotic is oxytetracycline. This antibiotic helps reduce the bacteria levels in the hive. Follow these steps for effective use:
- Mix the antibiotic as per the instructions
- Apply it directly to the brood nest
- Repeat the treatment weekly for three weeks
Always ensure you follow the label instructions carefully. This will ensure the health of your bees and prevent antibiotic resistance.
Natural Remedies
For beekeepers preferring natural treatments, several options are available. One effective method is the use of essential oils. These oils, like thyme and lemongrass, have antibacterial properties.
Here is how to use essential oils:
- Mix 10 drops of essential oil in 1 liter of sugar syrup
- Feed the mixture to your bees
- Repeat this process every week for a month
Another natural remedy is good hive management. Remove and destroy heavily infected combs. Replace them with new, clean foundation. This reduces the bacterial load and helps the colony recover.
Both antibiotic treatments and natural remedies have their advantages. Choose the method that suits your beekeeping practices best.
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to control pests and diseases in bee colonies. It combines multiple methods to minimize the use of chemicals. This is crucial in managing European Foulbrood (EFB), a serious bacterial disease affecting honeybee larvae. IPM aims to reduce the incidence of EFB while promoting bee health and sustainability.
Combining Methods
Combining methods is vital for effective IPM. Here are some strategies:
- Hygienic Practices: Regularly clean and disinfect beekeeping tools and equipment. This reduces the spread of EFB spores.
- Genetic Selection: Use bee strains known for their resistance to EFB. This can naturally reduce the disease’s impact.
- Biological Control: Introduce beneficial bacteria that compete with EFB-causing bacteria. This can lower EFB levels.
- Chemical Treatments: Use antibiotics as a last resort. Follow guidelines to avoid resistance.
Monitoring And Evaluation
Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential to IPM. This helps identify EFB presence early.
- Regular Inspections: Inspect hives frequently to catch signs of EFB early. Look for discolored larvae.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of hive conditions and treatments. This helps track the effectiveness of IPM strategies.
- Sampling: Collect samples from hives for laboratory analysis. This confirms the presence of EFB and helps plan treatments.
Monitoring results guide adjustments to IPM strategies. This ensures ongoing effectiveness and minimal impact on bee health.
| Method | Action | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Hygienic Practices | Clean tools and equipment | Weekly |
| Genetic Selection | Introduce resistant bee strains | Annually |
| Biological Control | Introduce beneficial bacteria | As needed |
| Chemical Treatments | Use antibiotics | When EFB detected |
Impact On Bee Colonies
European Foulbrood (EFB) significantly impacts bee colonies. This bacterial disease affects the larvae, leading to weaker colonies. Understanding the effects of EFB on brood and long-term colony health is vital for effective management.
Effects On Brood
EFB primarily targets the bee brood. The larvae become infected after consuming contaminated food. Symptoms include:
- Discolored larvae
- Twisted bodies
- Foul smell
Infected larvae often die before they can pupate. This results in gaps in the brood pattern, which weakens the colony. Beekeepers need to inspect their hives regularly. Early detection is crucial for managing EFB.
Long-term Colony Health
EFB not only affects the brood but also the long-term health of the colony. Weak colonies are more susceptible to other diseases and pests. The adult bee population may decline, leading to reduced honey production. Poor colony health can result in:
- Less honey yield
- Increased winter losses
- Higher risk of colony collapse
Effective management of EFB includes regular hive inspections and prompt treatment. Maintaining strong, healthy colonies is essential for successful beekeeping.
Case Studies
Understanding how European Foulbrood (EFB) is managed in real-world situations can offer valuable insights. Through various case studies, we can see practical applications of different treatment strategies. This section will explore successful management examples and lessons learned from beekeepers who have effectively dealt with EFB.
Successful Management Examples
Several beekeepers have shared their experiences with EFB. Here are some examples:
| Case Study | Location | Management Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Case Study 1 | Germany |
|
| Case Study 2 | France |
|
| Case Study 3 | Italy |
|
Lessons Learned
From these case studies, several key lessons have emerged:
- Regular monitoring is critical for early detection.
- Comb replacement helps to reduce infection spread.
- Combining chemical treatments with natural methods can be effective.
- Maintaining hive hygiene is essential.
- Quarantine of infected hives prevents contamination.
Each beekeeper’s experience highlights the importance of a proactive and multi-faceted approach to managing European Foulbrood.
Resources For Beekeepers
European Foulbrood (EFB) is a serious issue for beekeepers. Proper resources can make managing EFB easier. Here are some valuable resources to help beekeepers combat EFB effectively.
Educational Materials
Educational materials are crucial for learning about EFB. Books, articles, and online courses provide in-depth knowledge. Many universities offer free resources on bee health. These materials explain symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
Webinars and workshops also offer hands-on learning. Experienced beekeepers share their insights. This real-world experience can be invaluable. Seek out these opportunities to improve your knowledge base.
Support Networks
Support networks connect beekeepers with each other. Local beekeeping clubs are a great place to start. Members share experiences and advice. These clubs often host meetings and events.
Online forums and social media groups are also helpful. They offer a platform for questions and discussions. You can find support and solutions from beekeepers worldwide. These networks foster a sense of community and shared knowledge.
Future Directions
The battle against European Foulbrood (EFB) is ongoing. Beekeepers constantly seek better solutions. The future holds promise with new research and innovative practices.
Research Developments
Scientists are exploring new treatments. They study the bacteria Melissococcus plutonius. Understanding its behavior helps develop better control methods. Researchers are also examining the role of probiotics. These beneficial bacteria might protect bees from EFB. Early studies show promise.
Genetic research is another area of focus. Scientists aim to breed bees with natural resistance to EFB. This approach could reduce the need for chemical treatments. Less chemical use means healthier bees and honey. New diagnostic tools are also in development. Faster and more accurate tests help beekeepers take swift action.
Innovative Practices
Beekeeping practices are evolving. Some beekeepers use essential oils to combat EFB. These natural treatments show potential. Another innovative practice is improved hive management. Regular inspections and hygienic practices help prevent EFB. Using screened bottom boards can also reduce the spread of bacteria.
Education plays a key role. Beekeepers share knowledge through workshops and online forums. Staying informed about the latest practices helps everyone. Collaboration between researchers and beekeepers is crucial. Together, they find the best solutions for managing EFB. The future looks bright for healthier bees and more productive hives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is European Foulbrood?
European Foulbrood is a bacterial disease affecting honeybee larvae. It is caused by Melissococcus plutonius. This disease weakens bee colonies and can lead to significant honey production losses.
How To Identify European Foulbrood?
Symptoms include discolored, twisted larvae, and a sour odor from the hive. Infected larvae may appear yellow or brown. Monitoring and early detection are crucial for effective management.
What Treatments Are Available For European Foulbrood?
Treatment options include antibiotics like oxytetracycline. Beekeepers should follow local regulations. Regular hive inspections and good hygiene practices help prevent outbreaks.
Can European Foulbrood Be Prevented?
Prevention includes maintaining strong, healthy colonies and practicing good hive management. Regular inspections and hygienic practices are essential. Replacing old comb and avoiding the use of contaminated equipment also help.
Conclusion
Effective management of European Foulbrood is essential for healthy hives. Regular inspection helps in early detection. Clean tools and equipment to prevent spreading. Ensure strong, healthy colonies through proper nutrition. Utilize approved treatments when necessary. Consistent care leads to thriving bees.
Your effort ensures a productive and safe beekeeping experience. Keep learning and stay vigilant. Happy beekeeping!

